“Odorless Liquid Fertilizer” Demonstration in Yamaguchi Prefecture
– Rapid Fermentation Treatment of Dairy Manure Expected to Improve Farmland Conditions and Reduce Odor-Related Impacts on Tourism
JET Corporation (Head Office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; Representative Director: Tomoyuki Katayama), manufacturer and distributor of the ERS Rapid Fermentation Resource System, obtained verification results in October 2023 from Beru-chan-tachi no Ouchi Co., Ltd. (Shimonoseki City, Yamaguchi Prefecture), where the system was installed.
The results confirmed the successful production and field application of odorless liquid fertilizer made from dairy manure.
Following these results, JET has begun developing a compact fermentation unit specialized for liquid fertilizer production.
1. Background | Local Governments Concerned About Odors in Livestock Farming Areas
Livestock manure, when properly composted, can serve as a valuable agricultural resource such as fertilizer or soil conditioner.
However, when poorly managed or insufficiently fermented, it can generate strong odors and cause water pollution through runoff into rivers and groundwater.
Such environmental problems have raised growing concern among local authorities, especially in livestock-intensive regions.
Odor pollution not only affects working and living environments in the area but also impacts tourists unfamiliar with livestock odors.
As Japan seeks to promote regional tourism and inbound demand, it is essential to prevent such environmental nuisances.
To achieve this, there is a growing need for methods that allow high-quality composting and deodorization in a shorter time, minimizing the burden on livestock farmers.
2. Demonstration | Beru-chan-tachi no Ouchi Co., Ltd. (Shimonoseki City, Yamaguchi Prefecture)

In March 2023, Beru-chan-tachi no Ouchi Co., Ltd. installed an ERS unit to process dairy cow manure into liquid fertilizer.
Facing a decline in milk demand, the company introduced ERS not only to continue composting and bedding production but also to utilize its capability to generate odorless liquid fertilizer.
Producing liquid fertilizer without drying has reduced fuel consumption and overall costs.
After approximately six months of operation, in September 2023, the company confirmed stable processing performance and odor-free outputs, along with deodorization effects inside the composting facility.
Future plans include both on-site application and commercial sales of the liquid fertilizer.
Seasonal Variations in ERS Operation and Product Utilization
(1) April–November
- Method: Direct discharge of fermented material as liquid fertilizer.
- Advantage: Lower fuel consumption.
- Disadvantage: Larger volume of liquid output leads to higher evaporation and longer residence time in the composting area.
(2) December–March
- Method: Dry fermented material to prevent freezing; used as solid fertilizer (moisture content below 70%).
- Advantage: One-third the output volume compared to liquid fertilizer; shorter residence time in composting facility.
- Disadvantage: Higher fuel consumption.
Facility Overview
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Processed Material | Dairy cow manure |
| Processing Capacity | 25 tons/day |
| Equipment | ERS Type 5U |
| Output | Liquid fertilizer, compost |
| Location | Shimonoseki City, Yamaguchi Prefecture |
| Installation Date | March 2023 |
| Subsidy | Livestock and Dairy Profitability Enhancement Program (Facility Improvement Project) |
| Note | Member of Yamaguchi Prefecture Dairy Cooperative Association |
3. Features | Fast, Odorless, and Soil-Friendly – Even for Dairy Manure
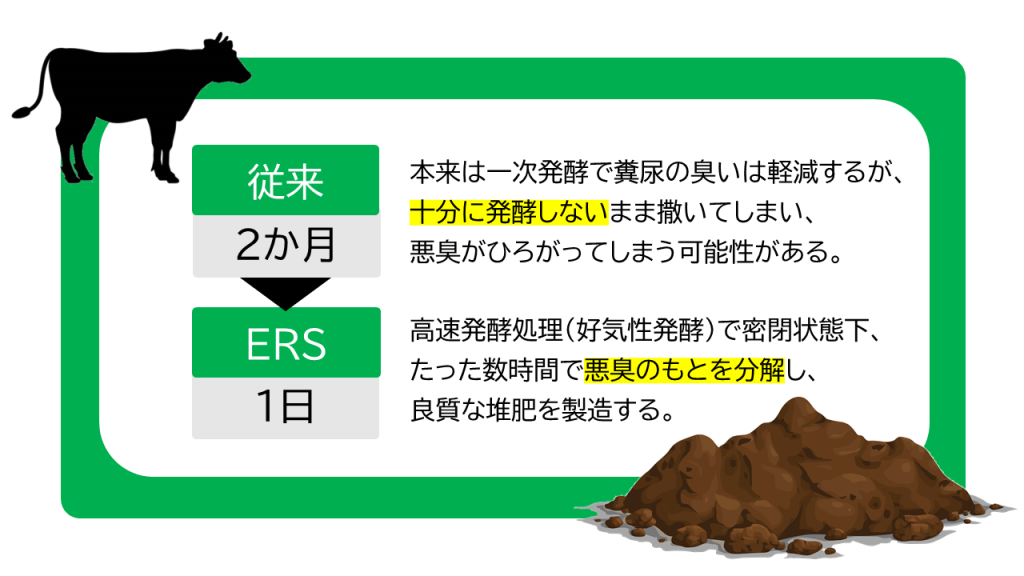
JET’s ERS (Rapid Fermentation Resource System) performs aerobic microbial fermentation, rapidly decomposing odor-causing substances within a few hours under sealed conditions.
For dairy manure that would normally require two months of composting, ERS produces odorless liquid fertilizer in just a few hours.
The resulting product meets high-quality standards, with an E. coli most probable number below 30 per 100g, ignition loss over 90%, and a C/N ratio of 12–15%, making it also suitable as compost with about 70% moisture content.
Unlike conventional methods that require sawdust addition for moisture adjustment, ERS does not use sawdust.
As a result, it achieves higher organic content and prevents long-term agricultural soil issues.
Additionally, ERS-treated materials do not cause groundwater contamination, addressing the rising environmental concerns associated with agriculture-related nutrient leakage.
Amid rising fertilizer prices, JET plans to obtain certification for this “odorless liquid fertilizer” as a special fertilizer and promote its commercial distribution.

The Five Key Benefits of Using ERS Liquid Fertilizer in Conventional Composting Facilities
- Aerobic Fermentation: Produces soil-friendly fertilizer highly demanded by crop farmers.
- Wastewater Reduction: Fermentation heat from microorganisms evaporates excess moisture.
- Odor Suppression: Fermented and sterilized fertilizer prevents odor generation in composting facilities.
- Shorter Fermentation Period: Minimal methane generation allows faster compost maturation.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Rapid fermentation reduces methane emissions derived from CO₂.
4. Outlook | Development of Compact Fermentation Equipment Specialized for Liquid Fertilizer Production
JET plans to release a new compact fermentation system specialized for liquid fertilizer production in spring 2024.
The unit eliminates the drying process, reducing equipment size and preventing wastewater generation.
For example, on a farm with 300 head of cattle operating four cycles per day,
a conventional 25-ton unit can be replaced with a 6-ton compact system, greatly reducing capital investment.
JET also plans to publish analytical data on the resulting products in upcoming reports.
The company remains committed to utilizing diverse organic wastes—such as municipal waste, diapers, sewage, sludge, livestock manure, vegetable scraps, food residues, construction waste, pruned branches, and other biomass—as valuable resources rather than disposal materials.
Through this approach, JET aims to maximize regional environmental efficiency and contribute to the realization of a circular economy.
About ERS
The ERS system uses indigenous microorganisms naturally present in the surrounding soil to sterilize, ferment, and dry organic matter within one day, converting waste into valuable resources.
The resulting low-moisture materials can be used as fuel, compost, fertilizer, feed, or bedding, helping achieve zero-emission operations.






